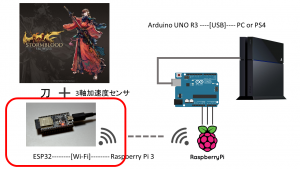
スマート刀で侍を遊ぶためのFF14用無線コントローラを作ろう計画、今回は刀側の無線デバイスであるESP-WROOM-32(以下ESP32)を触っていきます。
ESP32はArduinoIDEで開発できる無線チップで、Wi-FiとBLE(Bluetooth4.0)が利用できます。
今回はATOMとPlatformIOを使用して開発していきます。
ESP32の開発環境となるPlatformIOは、こちらのサイト(LOSANT – Getting Started with ESP32 and PlatformIO)を参考にしながら導入しました。こちらでは、セットアップ方法からPCとESP32のWi-Fi接続まで解説されています。
これで無線通信の準備が整いました。ラズパイへの通信方法はいくつか考えられますが、今回はHTTPを使って刀の動作をラズパイに送信します。
ESP32でデータをPOSTするために、HTTP系の処理をまとめたライブラリのHTTPClientを使うことにしました。
HTTPClientのインポートはこちらのサイト(techtutorialsx – ESP32: HTTP GET Requests)を参考にしました。
[2017/06/04 追記]
HTTPClientのPOST関数は送信完了までに3秒ほど間隔が空いてしまうことが判明したため、追加ライブラリなしで利用できてレスポンスの早いPOST方法を使うことにしました。新しいプログラムは本ページの最後に掲載します。
実際に書いたプログラムがこちらになります。
5秒おきに指定したURLに対して文字列をPOSTします。POSTする文字列を”SEND_DATA”としましたが、変数を入れることもできます。
#include "WiFi.h"
// WiFi credentials.
const char* WIFI_SSID = "###YOUR_SSID###";
const char* WIFI_PASS = "###YOUR_PASSWORD###";
// Internet domain to request from:
const char *sendServer = "192.168.###.###";
const int hostPort = 8080;
void setup() {
// Initilize hardware:
Serial.begin(9600);
// Giving it a little time because the serial monitor doesn't
// immediately attach. Want the firmware that's running to
// appear on each upload.
delay(2000);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Running Firmware.");
// Connect to the WiFi network (see function below loop)
connectToWiFi(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASS);
}
void loop() {
send();
delay(5000);
}
void send() {
WiFiClient client;
Serial.print("connecting to ");
Serial.println(sendServer);
if(client.connect(sendServer, hostPort)) {
String postMethod;
String postData = "SEND_DATA";
postMethod.concat("POST /");
postMethod.concat(".post HTTP/1.1\n");
postMethod.concat("Host: ");
postMethod.concat(sendServer);
postMethod.concat("\n");
postMethod.concat("Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
postMethod.concat("\n");
postMethod.concat("Content-Length: ");
postMethod.concat(postData.length()); //length of send data
postMethod.concat("\n\n");
postMethod.concat(postData);
postMethod.concat("\n\n");
client.print(postMethod);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(postData );
}
}
void connectToWiFi(const char * ssid, const char * pwd)
{
// https://www.losant.com/blog/getting-started-with-esp32-and-platformio
// Connect to Wifi.
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
// Set WiFi to station mode and disconnect from an AP if it was previously connected
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.disconnect();
delay(100);
WiFi.begin(ssid, pwd);
Serial.println("Connecting...");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
// Check to see if connecting failed.
// This is due to incorrect credentials
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECT_FAILED) {
Serial.println("Failed to connect to WIFI. Please verify credentials: ");
Serial.println();
Serial.print("SSID: ");
Serial.println(ssid);
Serial.println();
}
Serial.println("...");
delay(3000);
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.println("connected");
}
サーバ上でPOSTされた文字列を受け取ることができました。あとは加速度センサのパターンを定数化すればクライアント(刀)側のソフトは完成です。
次回はサーバ側(ラズパイ)の設定をしたいと思います。
>> 無線デバイス制御編その2 Node.js
記載されている会社名・製品名・システム名などは、各社の商標、または登録商標です。
Copyright (C) 2010 – 2017 SQUARE ENIX CO., LTD. All Rights Reserved.
[2017/06/04 変更プログラム]
追加の外部ライブラリなしで動作します。
動作内容は上で紹介したものと同一です。送信開始から終了までにかかる時間は数ms程度に短縮されました。
#include "WiFi.h"
// WiFi credentials.
const char* WIFI_SSID = "###YOUR_SSID###";
const char* WIFI_PASS = "###YOUR_PASSWORD###";
// Internet domain to request from:
const char *sendServer = "192.168.###.###";
const int hostPort = 8080;
void setup() {
// Initilize hardware:
Serial.begin(9600);
// Giving it a little time because the serial monitor doesn't
// immediately attach. Want the firmware that's running to
// appear on each upload.
delay(2000);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Running Firmware.");
// Connect to the WiFi network (see function below loop)
connectToWiFi(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASS);
}
void loop() {
send();
delay(5000);
}
void send() {
WiFiClient client;
Serial.print("connecting to ");
Serial.println(sendServer);
if(client.connect(sendServer, hostPort)) {
String postMethod;
String postData = "SEND_DATA";
postMethod.concat("POST /");
postMethod.concat(".post HTTP/1.1\n");
postMethod.concat("Host: ");
postMethod.concat(sendServer);
postMethod.concat("\n");
postMethod.concat("Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
postMethod.concat("\n");
postMethod.concat("Content-Length: ");
postMethod.concat(postData.length()); //length of send data
postMethod.concat("\n\n");
postMethod.concat(postData);
postMethod.concat("\n\n");
client.print(postMethod);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(postData );
}
}
void connectToWiFi(const char * ssid, const char * pwd)
{
// https://www.losant.com/blog/getting-started-with-esp32-and-platformio
// Connect to Wifi.
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
// Set WiFi to station mode and disconnect from an AP if it was previously connected
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.disconnect();
delay(100);
WiFi.begin(ssid, pwd);
Serial.println("Connecting...");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
// Check to see if connecting failed.
// This is due to incorrect credentials
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECT_FAILED) {
Serial.println("Failed to connect to WIFI. Please verify credentials: ");
Serial.println();
Serial.print("SSID: ");
Serial.println(ssid);
Serial.println();
}
Serial.println("...");
delay(3000);
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.println("connected");
}